| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: |
|
2019年5月16日 星期四
[Python]Numpy linspace 的使用方法
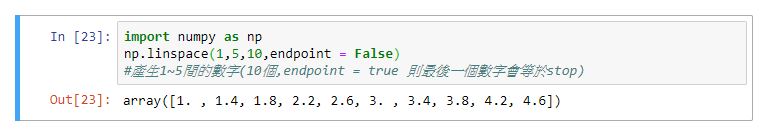
numpy.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None)
實作:
訂閱:
張貼留言 (Atom)






沒有留言:
張貼留言